Nebulae are known for their attractive colors and stunning landscapes that fill the space. It has been a source of question for many years for astronomers, dazzling them with its colors and shapes, and raising their questions about its components and origins.
What is a nebula?
The nebula is massive masses of gases and dust; Some of them were formed as a result of the explosion of a star at the end of its life, such as what is known as a supernova, while others are a starting point for the formation of new stars, which are called "star nurseries".
Nebulae consist mainly of hydrogen and helium gases, and these gases spread in space very quickly and over vast areas. However, gravity limits the velocity of these gases, and they start to form large masses of gases and dust. The larger these blocks, the stronger their attractiveness.
Nebulae are spread in outer space, and are mainly found in interstellar space, and they appear in irregular shapes. But it is distinguished by its dazzling colors and attractive shapes.
Types of nebulae
The Dark Nebula: It is a giant cloud of cold gases and dust that does not emit any light; Therefore, the dark nebula hides within it the stars it contains, so they are not apparent because of its darkness.
Diffuse reflecting nebula: These nebulae consist of a large proportion of hydrogen gas in addition to some dust, and they reflect light to the stars that contain them, which are the stars closest to them. Dust contributes to the blue color of these nebulae. The Thuraya group is a perfect example of the Blue Nebula.
Diffuse emission nebula: These are described as emitting nebulae. Because it radiates its own light; This is because the hydrogen atoms, which are its main component, are affected by the strong ultraviolet rays emitted from nearby stars, and this is what makes them ionize - that is, the hydrogen atom loses its only electron and emits a photon - resulting in the emission of lights from the nebula.
Planetary Nebula: When a diffuse nebula is coupled with the birth of a new star, the planetary nebula forms the remnants of that star. The planetary nebula has this name. Because it has circular sides.
The most famous nebulae in space
Helix Nebula: This nebula, also known as NGC 7293, is the closest nebula to Earth, except that it is about 700 light years away. It was discovered by the scientist Karl Ludwig Harding before 1824; It may be the result of a star exploding.

The Cat's Eye Nebula: It is a planetary nebula about 3262 light years away from Earth, and it is located in the constellation of the Dragon. Discovered by William Herschel in 1786, it is the most luminous nebula in space. It was one of the first nebulae to study its spectrum, and this was by William Higgins in 1864.
The Butterfly Nebula: The Butterfly Nebula is 4,000 light years away from Earth and is located in the constellation of Scorpio. It was discovered by astronomer Rudolf Minkowski in 1947. The Butterfly Nebula has two wings that were formed by the expiration of a star estimated to be five times the size of the sun. The Butterfly Nebula is surrounded by giant clouds of dust that emit ultraviolet rays.
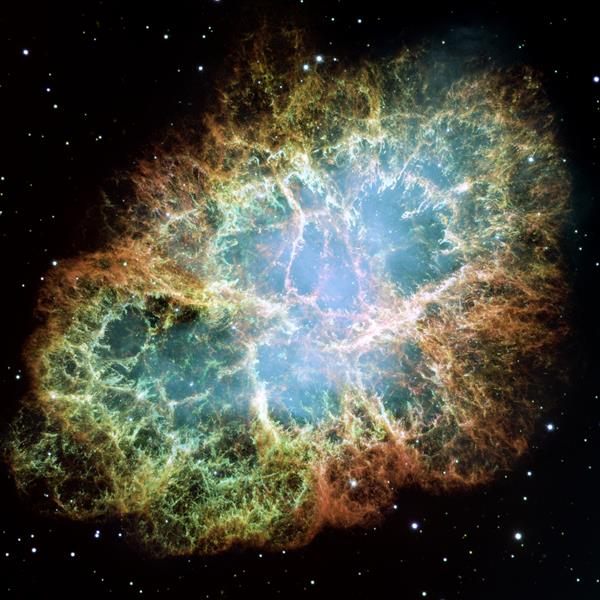
The Crab Nebula: The Crab Nebula is about 6,523 light years from Earth and is located in the constellation Taurus. The Crab Nebula is the first celestial body detected as a supernova explosion. The nebula is filled with many mysterious filaments that are distinguished by their lightness and great speed.
The Falcon Nebula: It is considered one of the most beautiful nebulae in space. The nebula is about 7,000 light-years away from Earth and is located in the constellation of the Snake. This emission nebula contains a number of energetic stars that help form gases and dust.
References
spaceplace.nasa.gov
astronoo.com
astronomyisawesome.com
read also :

Comments
Post a Comment